Okay, this got me curious. From the wikipedia article on viruses:
Viruses are considered by some biologists to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce, and evolve through natural selection, although they lack the key characteristics, such as cell structure, that are generally considered necessary criteria for defining life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as “organisms at the edge of life” and as replicators.
Theoretical biologist here. I consider viruses to define the lower edge of what I’d consider “alive.” I similarly consider prions to be “not alive,” but to define a position towards the upper limit of complex, self-reproducing chemistry. There’s some research going on here to better understand how replication reactions (maybe encased in a lipid bubble to keep the reaction free from the environment) may lead to increasing complexity and proto-cells. That’s not what prions are, but the idea is that a property like replication is necessary but not sufficient and to build from what we know regarding the environment and possible chemicals.
I consider a virus to be alive because they rise to the level of complexity and adaptive dynamics I feel should be associated with living systems. I’ll paint with a broad brush here, but they have genes, a division between genotype and phenotype, the populations evolve as part of an ecosystem with all of the associated dynamics of adaptation and speciation, and they have relatively complex structures consisting of multiple distinct elements. “Alive,” to me, shouldn’t be approached as a binary concept - I’m not sure what it conceptually adds to the discussion. Instead, I think it should be approached as a gradient of properties any one of which may be more or less present. I feel the same about intelligence, theory of mind, and animal communication.
The thing to remember when thinking about questions like this is that when science (or history or literature…) is taught as a beginner’s subject (primary and secondary school), it’s often approached in a highly simplified manner - simplified to the point of inaccuracy sometimes. Many instructors will take the approach of having students memorize lists for regurgitation on exams - the seven properties of life, a gene is a length of dna that encodes for a protein, the definition of a species, and so on. I don’t really like that approach, and to be honest I was never any good at it myself.
Thanks for posting this! While my knowledge of biology is quite limited, it’s always great to get an informed person’s take on an interesting topic.
Interesting, thanks! I’m someone that has been educated on viruses to a Radiolab level, and as such I’d like to hear your take on the idea that viruses used to be more complex organisms, which then evolved to be the simple and efficient form they are now.
Wildlife biologist here, and I have to concur with just about all of this.
I think we generally look at a viruses and consider them alive but just barely. While prions are not because they (proteins) are what is considered one of the building blocks for life. Self replication being one of the major criteria we’d look for. We look at a very macro level of life but our education and work has a strong overlap down here a well.
This is such a well written post! Gets the point id like to make across in a much better way than I could
They’re not compromised of cells, can’t self regulate, and can’t replicate on their own and other organisms have to do that for them. The last point being important to our criteria for living. I was never taught as a biologist by anyone that they were alive
o7
“Obligate intracellular parasite” was drilled and showed up on multiple exams, along with all that you mentioned. I’ve also heard “escaped cellular machinery.”
Absolutely fascinating…if a tad frightening.
There are plenty of organisms we generally consider “alive” that can’t replicate or do other key functions without other organisms.
Like what? Sorry my comment posted so many times my phone was messing up
For reproduction purposes, many parasites require a specific host to reproduce in. An interesting example is a worm that mind controls a snail and gets itself eaten by a bird, and then reproduces in the bird. Surprisingly, both the snail and the bird survive this process. (Granted, the difference between this and a virus is the virus uses the RNA decoding infrastructure in the infected cell to reproduce itself, while a parasite just is adapted to reproducing in the environment of the hosts body, but uses its own cells to do the reproduction).
However, there are many, many examples in nature of some essential task (often some part of the energy production/absorption process) that are done by a different organism. Some particularly interesting examples:
-
there are a handful of animals that eat plants, absorb the chloroplasts, and use those to do photosynthesis
-
In most animals, even in humans, a lot of the digestion process is done by bacteria living in your digestive tract. Some illnesses are caused by issues with the digestive tract bacteria, such as them dying out.
There are other animals adapted to living in environments or using things produced by other organisms. Hermit crabs get their name from their behavior of borrowing shells created by other organisms.
Really the only organism that can truly live “by itself” would probably be something like algae.
-
deleted by creator
deleted by creator
deleted by creator
Are these requirements for your definition of life? Is it possible for us to reproduce without relying on other organisms?
There you go defining humans as not alive again
Worth mentioning: life is a construct created by humans. We decide if it’s alive, just like we decided if anything else was alive. There’s no definite answer that science can provide on this topic. It can only provide humanity with more facts with which we can contrive a distinction.
We’ve given life a set of repeatable rules that create a definition. Viruses don’t meet the rules.
Yes, everything is a social construct and reality is fake and bad
I’m no scientist but I’d say, “Do it reproduce? Do it evolve? Do it try to survive? Bruh, it’s alive.”
I’m no scientist though. Just an idiot watching thangs. :p
Do it reproduce?
Not by themselves, no. They need to take over a cell’s replication machinery for that.
Do it evolve?
Yes, as they are subject to natural selection.
Do it try to survive?
I don’t think so, they don’t try anything to do anything, they just are… but the same can probably be said for most actually living organisms, including many relatively complex ones, so I don’t think it can be used as a way to determine if something is alive or not.
But it did reproduce then no? Its just like how some organisms are surviving as a parasite. They need another thing to survive mostly as food. But in this case, as a reproduction method.
The thing, though, is… you take a virus, put it in a petri dish by itself, and it does… nothing.
It doesn’t have a metabolism, it doesn’t look for a host, it doesn’t do anything… it’s just an inert clump of organic matter. (Then again, probably the same could be said for, say, spores. Or pollen. Or raw DNA or even RNA. Are those alive…?)
But plug it into a cell and… well, it sort of breaks apart, injecting it’s RNA or DNA into the cell, and… that’s it for that particular instance of the virus.
Sure, the cell will then take that genetic payload and unwittingly use it to fabricate as many copies of the virus as it can… but at that point the original virus instance is just an empty protein husk… is it still alive…? Does “being alive” maybe not apply to individual virus particles, but to this whole process…?
Maybe being alive is not just a binary, but a scale (or something more complex) where you can fit anything from crystals or prions to us and who knows what else, maybe whole ecosystems, maybe the Gaia concept of a living world…
But we humans certainly do seem to like our black and white binary choices, even if viruses might be a triangular peg we’re trying to fit into either a round or square hole…
I agree, the point is that we need to define “alive” itself clearly which as you stated, is currently beyond our understanding.
If being inert constitutes as not living then yes, virus is not alive. Their “evolution” is not because of their doing/needs but rather due to their construction. In that case I think virus is more akin to a poison. The substance itself can be not dangerous, but due to a metabolism process inside a specific organism/cell, it becomes a dangerous substance. The side effect in this case is just so happens to make another copy of the virus. But this process is prone to mutation as their building block is quite prone to do so, and we get the “evolution”.
Yours is the reply I like the most.
Most interesting definition, I think, comes from contrapposto. Can it die? No. So long as it retains its “shape” more or less, it functions. If heated or denatured, it no longer functions. More like broken than dead.
It seems to fail the last criteria there. They don’t actively escape or react to predation. For the most part they aren’t actively “trying” anything other than to just float around and replicate.
It can’t reproduce on its own, though. It needs a living cell to do that.
Perhaps an artifact from an earlier abiogenesis event that cannibalized itself before our own evolutionary tree started?
I believe the theory is that viruses have evolved from other life forms multiple times. Basically a DNA sequence gone rogue.
Like if your computer got a glitch that caused it to burn CDs that, when inserted into another computer, gave it a glitch that caused it to burn CDs that, when inserted into another computer, etc.
This explanation is excellent but feels incomplete. What happens after it burns the CD?
It runs out of all CDs and thus stops working. A PC can not work without CDs.
ok i’m not a biologist but having a cell structure as a prerequisite for defining life sounds very arbitrary to me.
fungi are extra alive somehow
I swear Fungi are an alien species, they’re so weird
deleted by creator
What are you talking about? I’d like a citation for that.
DNA in all eukaryotes is composed of adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. RNA in eukaryotes subs in uracil for thymine.
There are things that make them substantially different from other branches of life, but not in that way.
Absolutely not true. Fungi are weird but not this weird. Citation please
How so?
Some have features of both plants and animals, so they’re kinda hard to fit into rigid categories.
they’re neither plants or animals, so… what does that have to do with being extra alive
That’s how I interpreted @moosetwin@lemmy.dbzer0.com ’s “extra alive” phrasing. If you want to know exactly what they meant, I recommend asking them.
🚨 Viral meme detected
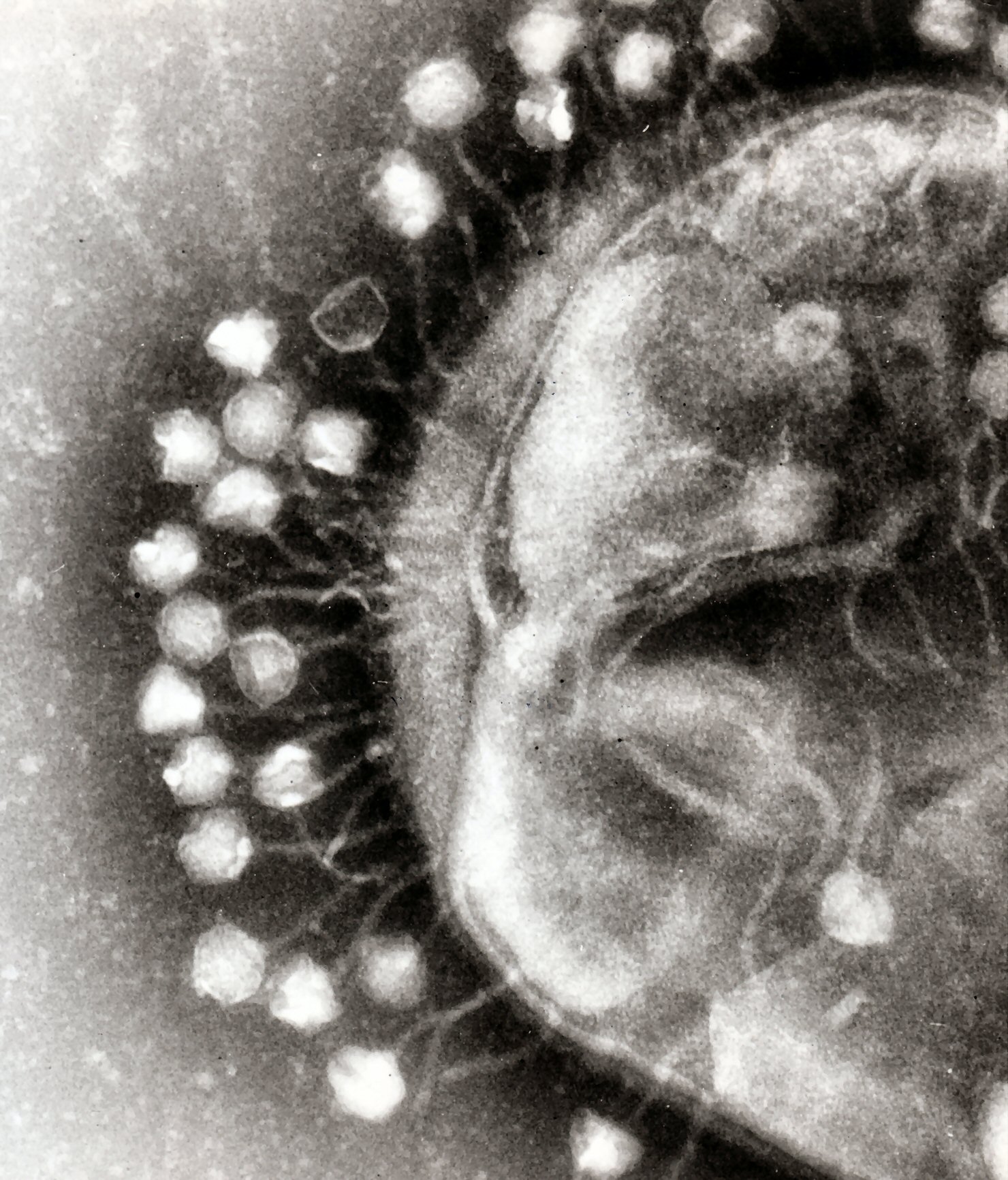
Is this what some virus really looks like? It looks like Tron-era CGI.
The image is in fact CGI, but yes there are several viruses known as bacteriophages that look like this.

Trying to find this confirmed electromagnetic scan of this phage led me down a truly fascinating rabbit hole about antibacterial phage therapy, taxonomy, and more. Let your curiosity take the better of you on Wikipedia
Such awesome pictures
Let’s all take a moment to appreciate the 3D artist that was given the task to make this image, probably looked up a bunch of grainy references and then delivered this kick ass render.
At this scale we’d be seeing with electrons not photons, and everything would be gold coated. It’s unlikely the head would be transparent. But other than that, not bad. False color gets applied to the B&W EM images, which helps.
Rabies is shaped like a bullet!


hmm yes rabies looks like a bullet because once you are shot with it you are dead
That was my takeaway too. I knew Ebola was a big long shape, so it didn’t stand out much, but then “ohhh of course rabies just randomly looks like invisible nano bullets!”
Dannng. Cool reference pictures, thanks for sharing.
Complex viruses seem almost too complex to function. Just from a human lead engineering standpoint, I can see so many points of failure
Viruses throw dung at the wall and see what sticks.
A real life genetic algorithm, essentially.
Artist’s view of bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria and look like this. They attach to the bacterial wall with these fibers that look like spider legs, and then inject their DNA into the bacteria by contracting the sheath that attaches to the DNA-containing head. They kinda work like a syringe.
They almost seem like just a “living” reproductive system, as if that’s the entirety of their existence. Like real-life Daleks going “IN-SEM-IN-ATE!”
Yes, this is a bacteriophage. Truly fascinating stuff I’m lucky to work with every day.
More or less yes, that’s the type of virus we learned about in biology class at least. Although there are various shapes a virus can have. Like covid that is round or other viruses that look more like bacteria.
Would you prefer it to have a little hat and mysterious (and unnecessary) white gloves ?
Yes, I’ve always thought of bacteriophages as giant death robots of the virus world
Evidence of a false dichotomy to me
The third thing would be “inanimate”
Which is essentially Latin for “not alive” so 🤷♂️
There’s a difference between dead and non-living though. Dead implies it was alive previously
Maybe undead ? That would explain all those viral zombie apocalypses.
Do prions count as another secret fourth thing?
Nah they’re a single molecule. While they do have a mechanism to “reproduce”, they cannot react to stimuli of any kind, or evolve. Of the 7 commonly accepted traits of life, viruses have 5-6 depending on where you stand with them not being able to reproduce on their own. (In comparison, while a tapeworm or other parasite might need a host, they bring their reproductive equipment with them).
Prions have 1 of those traits. They can’t regulate an internal environment as they cannot have one, they lack any kind of organizational trait, they have no metabolism (the other one viruses lack), they do not grow, they don’t adapt to their environment, and they do not respond to stimuli.
A digital thermometer has organization and responds to stimuli, so it’s more alive than a prion.
Actually they can evolve, though I assume the range of evolution would be much narrower than traditional life forms, even viruses.
Interesting.
The paper indicates the forms are specifically limited, in mice there were 15 specific forms they could take.
But still, they evolve between the forms, so yeah, they are equally alive as a digital thermometer. Now they just need to get their act together to beat a tamagotchi.
If viruses aren’t alive because they don’t have their own reproductive equipment, then neither are men
Evolution came up with sexual reproduction as a mechanism to keep the gene pool varied and varying. In this sense the female and male sexual organs constitute one single reproductive apparatus.
Another ingenious mechanism is the bee/flower or fly/flower or bat/flower, duos of completely separate species in beautiful, poetic symbiosis. Birds with seeds is another one.
The bees (or flies or bats) reproduce on their own, but the flower has turned those species into part of its’ own reproductive organs, in a way.
Removed by mod
I found this to be interesting. The word (and concept) of a virus predates its actual discovery by over 500 years.
The English word “virus” comes from the Latin vīrus, which refers to poison and other noxious liquids. Vīrus comes from the same Indo-European root as Sanskrit viṣa, Avestan vīša, and Ancient Greek ἰός (iós), which all mean “poison”. The first attested use of “virus” in English appeared in 1398 in John Trevisa’s translation of Bartholomeus Anglicus’s De Proprietatibus Rerum. Virulent, from Latin virulentus (‘poisonous’), dates to c. 1400. A meaning of ‘agent that causes infectious disease’ is first recorded in 1728, long before the discovery of viruses by Dmitri Ivanovsky in 1892.
Removed by mod
So what about ‘Mastercard’?
Un-PC, that’s what!
I wonder what they’ll change the name to.
‘Bosspersoncard’
It passed through the bacteria filters! So small that it passes by the filters and it kills–poison, toxin. But wait, it can be diluted to lowest effective concentration, and then with addition of host it grows back to high concentration. What poison does that?
I can’t find anything on the 1728 claim, but I remember hearing that Louis Pasteur coined the term while studying rabies in the 1880s!
deleted by creator
This little doodad reminds me of Jenova Chen’s old freeware game flOw. Fun little game, but iirc it isn’t free anymore.
Love his games, Journey is still one of my top 10 gaming experiences of all time.
I loved flOw and Flower, but I still haven’t played Journey, I need to get a good ps3 emulator just for that. Also I just checked and the 2006 “student” version of flOw is still free, the 2007 ps3 version is paid.
Its in steam now and works even better than the original ps3 version! Its also 70% off right now :0
Ehhh I guess I need to figure out steam/proton then lol. I haven’t played games in years. Is Flower up there too?
Edit: Thanks for all the advice on steam/proton everyone!
Not much to figure out, just make sure to not get the flatpak/snap. Any non-arcane distro should have a working package, the trick to packing steam being not trying to be smart about things you basically have to give it a libc, gpu, and FHS (chroot or not), it takes care of everything else.
This should not be seen as advice for anyone but a very small number of people:
There is a good purpose for the flatpak. My use for it is Squad’s anti-cheat uses I think a depricated function in C, and the most updated version of glibc doesn’t support it anymore. The flatpak does contain a version of glibc that works, so I have two versions of Steam installed on my system. I only use the flatpak for Squad, because that’s the only game with that issue.
In principle steam should be able to manage such things by using a different runtime for the game.
It is! They’re both steam deck verified so they should run on proton!
The vast majority of games on Steam will just work when you hit play on Linux. There’s not much to figure out. You just need to create an account, download the launcher, and purchase the game. You shouldn’t have an issue figuring it out. If you do, feel free to ask for help.
The replicators are real. I still think the version from Stargate SG-1 are the scariest though.
Ok protein spooder
Isn’t metabolism one definition of life? If so, they’re not alive.
They actually don’t have a metabolism, that’s why they don’t fall into the definition of life in the first place.
Source Wikipedia: “Although they have genes, they do not have a cellular structure, which is often seen as the basic unit of life. Viruses do not have their own metabolism and require a host cell to make new products. They therefore cannot naturally reproduce outside a host cell”
Man, all these biologists going on about cell structure are in for a rude awakening when we run into silicon based life forms. Or even Commander Data
A rude awakening? Maybe. But a fascinating one!!
Why can’t they be fascinated and produce a universalisable definition now? How am I supposed to trust their opinion of whether a virus is alive if they can’t even get Commander Data right? Commander Data is way easier to philosophically understand than a virus.
Sorry, I’m unfortunately too much of a literal, analytical thinker to continue this line of joking. Maybe I don’t even fall into the definition of life myself, who knows…
I’m not joking, I genuinely disagree with the mainstream classification of viruses and Commander Data is genuinely an important cultural symbol for these issues.
Ah OK, I couldn’t tell. So what would you say would be a better definition and what would you like to see included? I’m not really familiar with Data, maybe some background would be helpful…
You commented twice
They’re checking the ‘can reproduce’ box for whether their comment alive or not.
Weird, i didn’t even got a server timeout, which is usualy the cause.
Viruses are Schroedinger’s cat confirmed